Tag: vaccinations
If caught and symptoms develop, rabies is almost invariably fatal.
Rabies is spread through the saliva of an infected animal and is present in over 150 countries worldwide. Up to 100 children die each day from rabies, and more than 55,000 people a year are killed from the disease, mainly in Asia and Africa.
If bitten or scratched by an infected animal you need to act quickly. Your pre-exposure vaccines simplify medical care in case of a potential rabies exposure, reducing the number of post-exposure vaccine doses needed and providing more time to seek medical care because your antibodies will start to respond. This is crucial when traveling to remote areas with limited access to medical facilities.
If you haven’t had pre-travel vaccinations, the treatment is much more complicated; it is also expensive and can be hard to access in lower income countries. If treatment is given correctly and promptly after exposure, it is 100% preventable.
It is extremely important that if you are travelling somewhere with a known risks of rabies it only seems sensible to protect yourself against it. Rabies is a vaccine-preventable disease, so make sure you get vaccinated before you travel.
For more information on rabies and travel health, visit our rabies page here.
The Fleet Street Clinic is passionate about travel. We have provided rabies vaccinations for over 20 years. Our team of expert travel medical professionals provide advice and detailed consultations to ensure you have a healthy trip.
You can book a travel consultation or rabies vaccination appointment online.
I picked up Covid early in the pandemic and put my newly acquired immunity to good use by joining the Covid medical team at my local hospital for the weeks that followed. There was a side-effect however: a sense of invincibility that has perhaps made me take less care to protect myself from respiratory viruses ever since.
My luck ran out recently while looking after a group of patients with upper respiratory infections. Not all respiratory viruses are equal: we may call them “colds”, but some varieties are considerably more unpleasant than others.
Using PCR, we can now tell the difference between 22 different bugs with pinpoint accuracy, in about an hour. Mine turned out to be parainfluenza type 1 (there are four serotypes, who knew?) – a nasty virus, more common in the USA and among children.
My bout ranked alongside my experience with Covid: the symptoms lasted over three weeks and included a secondary lower respiratory infection requiring antibiotics to clear.
There’s no vaccine as yet against parainfluenza, but there are vaccines against other important respiratory infections – pneumococcal pneumonia, RSV, Covid-19, a newly-recommended adult top-up against whooping cough, and of course flu.
I shall be having all of these vaccines this winter and will take much greater care to protect myself when those around me have “colds”.
STUDENTS URGED TO GET VACCINATED BEFORE UNIVERSITY
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA), formerly known as Public Health England, is encouraging students to get vaccinated before they start/ return to University to protect themselves against a range of life-threatening illnesses.
Starting university and attending Fresher’s Week exposes students to a host of viruses and bacteria – some of which for the first time.
First year or returning students can be at increased risk of serious diseases such as meningitis, septicaemia and measles as they mix with large numbers of other students from around the country and overseas.
We strongly advise the following 3 vaccinations at a minimum for students:
Meningococcal ACWY (MenACWY)
– Protects against 4 common strains causing meningitis and septicaemia
Measles, Mumps and Rubella (MMR)
– Protects against measles, mumps, rubella
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
– Protects against HPV-related cancers including cervical, penile & throat cancers, alongside protection against genital warts. HPV vaccination is estimated to prevent up to 90% of HPV-related cancers.
Meningitis Vaccinations:
– Meningococcal ACWY (MenACWY)
– Meningococcal B (MenB)
UKHSA vaccine coverage data shows around 1 in 8 new students going to college and university this year remain unprotected against these 4 strains of meningococcal bacteria, each of which can cause long term disability, serious health complications and can be life threatening.
The MenACWY vaccine is given by a single injection into the upper arm and protects against four different strains of the meningococcal bacteria that cause meningitis and blood poisoning (septicaemia): A, C, W, and Y. You can book online.
The MenB vaccine is also given as an injection to the upper arm but is a 2-dose course for full protection. It protects agains the B-strain of the meningococcal bacteria. You can book online.
Cases of meningitis, particularly virulent strain Men W & Men B, have been rapidly rising amongst students since 2009.
What is Meningitis W?
Meningitis is a bacterial infection of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Meningococcal meningitis (Men W) is a highly serious form of bacterial meningitis that can lead to septicaemia. It is spread by droplets that come from a person who is infected with the bacteria.
Although the strain is most likely to affect babies, statistics reveal that older children, teenagers, and adults are also at risk. In recent times, cases amongst normally healthy teenagers have spiked and the fatality percentage is higher with Meningitis W than it is with the most common strains, Meningitis B and C.
Meningitis can progress quickly leading to blood poisoning (sepsis), which can kill within 24 hours. So, it is important to know the signs and symptoms of meningitis and septicaemia (sepsis).
Early symptoms of Meningitis include:
- headache
- a high temperature (fever)
- being sick (vomiting)
- a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it (but a rash will not always develop)
- a stiff neck
- a dislike of bright lights
- cold feet and hands
- or muscular pain
Sepsis is a life-threatening reaction to an infection. It happens when your immune system overreacts to an infection and starts to damage your body’s own tissues and organs. Symptoms can be vague but include:
- acting confused, slurred speech or not making sense
- blue, pale or blotchy skin, lips or tongue
- a rash that does not fade when you roll a glass over it, the same as meningitis
- difficulty breathing, breathlessness or breathing very fast
Many people confuse the symptoms with just a hangover or freshers’ flu, which is one of the theories as to why students are so high-risk. So, check-in on your friends who are unwell. Symptoms can progress rapidly so urgent action in getting medical attention is critical – call NHS 111 straight away
Protection against this strain of Meningitis W is provided through the Meningitis ACWY vaccine. Only one dose is required.
We also carry an excellent stock of the Meningitis B vaccine and can provide both vaccinations at the same time should you require it.
Book your MenACWY & MenB vaccination appointment online
Measles, Mumps and Rubella (MMR) Vaccination
Mumps is a highly contagious viral infection which is spread in the same way as the flu. Coughing, sneezing and kissing can rapidly spread the infection, especially in the close quarters of student accommodation.
Measles is a very infectious viral infection which is also spread by coughing and sneezing. There have been multiple outbreaks of Measles around the world including the UK this year, so it’s important to make sure you are protected as you socialise with new peers.
Both Mumps and Measles can be prevented by safe and effective vaccination, MMR.
Book your MMR vaccination appointment online
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccination
HPV is a common virus that is passed on via genital contact. There are more than 100 HPV types which infect genital areas. Sometimes they cause no harm and the infection can go away on its own. However, the virus can persist and cause cells to change which can lead to some forms of cancers; cervical, head, neck & throat or genital warts. More information on HPV can be found here.
The HPV vaccine is offered at our clinic for girls and boys to protect against HPV-related cancers and genital warts. Book your HPV vaccination appointment online
Other vaccinations that we recommend for students starting/ returning to University are:
Fresher’s Flu:
Every year different flu strains circulate and infect millions of people. Being exposed to a new pool of infections in University accommodation can increase the risk of catching the flu. Having the flu jab before you go to University will help protect you against the flu and stop you getting sick.
Flu jabs become available from 3rd September and can be booked online.
BCG:
If you are from outside the UK, you should be vaccinated against tuberculosis (TB) before you enter the UK. A weakened strain of tuberculosis, the BCG Vaccine, is injected to protect against the infection. Those unsure of their immunity can have a simple Mantoux test to confirm.
Book your BCG vaccination or Mantoux Test appointment online
Tetanus:
Tetanus is a rare condition caused by bacteria entering a wound. We recommend making sure you are up to date with your DTP vaccinations and boosters before leaving for university. This vaccine protects against tetanus as well as Diptheria and Polio. Don’t let a cut or burn ruin your freshers week.
Book your Tetanus vaccination appointment online
Wellness VACCINATIONS AT FLEET STREET CLINIC
Fleet Street Clinic offers a friendly environment and a team of experienced medics to administer all wellness vaccinations. We meet rigorous quality management standards to ensure we offer you the highest standards of clinical care: you can feel confident you are in safe hands.
Secure your peace of mind by ensuring you are protected. Get your vaccines before university starts to receive protection in time.
Book your vaccination appointment today
_____________
For the full The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) statement, click here.
Albania, located in Southeastern Europe, is a tourist haven this time of year.
Albania has much to offer, from stunning mountain scenes to crumbling castles to picture-perfect beaches all with easy-going charm and a friendly atmosphere. Right now the tales of its beauty haven’t quite reached the masses, but we have a feeling this is likely to change in the not too distant future.
If you plan on staying in Albania‘s capital, Tirana, be sure to see the rotating restaurant/ bars for spectacular city views. Or take to the countryside and seashores to take in the ubiquitous sight of the abandoned concrete bunkers of Albania. Fearing invasion during the Cold War, Albania’s leader Enver Hoxha forced his country to build tens of thousands of bunkers throughout the country. These days you’ll see most in a state of slow decay but some have been given a new lease of life as a hotel, home or museum.
Visit Berat, to see the ‘town of a thousand windows’. This fascinating city dates back to the Ottoman Empire. The most striking feature of Ottoman architecture is the collection of whitewashed houses and towering minarets which adorn the hill to its castle. It is easily a highlight of visiting Albania. If, however, you prefer the great outdoors scale the peaks and troughs of the Accursed Mountains and take in the captivating castles of Gjirokastra.
Whatever your plan to do, be sure to follow our top travel tips to stay healthy in Albania.
Routine Vaccinations
All travellers to Albania are advised to be in-date with their routine immunisations. These include diphtheria-tetanus and polio and measles, mumps and rubella. Europe has seen huge outbreaks of measles in recent years. Therefore, all travellers should make sure they have received at least two doses of the vaccination, MMR.
If you’re unsure of your immunity, you can have a simple blood test to find out. Some travellers may wish to consider vaccinations for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B, Rabies, and Tick-Borne Encephalitis. It is best to book a pre-travel consultation with a travel nurse to discuss your holiday plans. Together you can discuss what vaccines you’ll need.
Trekking and Ticks
The dramatic peaks of the Accursed Mountains spread their spoil between Kosovo, Albania and Montenegro. Those who plan to take advantage of the great outdoors should strongly consider vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis (TBE). TBE is a bacterial infection spread via tick bites or the consumption of unpasteurised dairy produce (between spring to autumn). Contracting the illness causes a fever with neurological complications.
TBE is vaccine-preventable and consists of 2 doses of the vaccination being given at least 2 weeks apart. A third dose is given 5-12 months later to give longer-term protection. Travellers should also avoid ticks by wearing long trousers and socks, and using DEET insect repellant. If you spot a tick on you, it needs to be removed promptly with some flat tweezers or a tick remover and cleaned with alcohol to reduce the risk of infection.
Rabies
Rabies is a fatal virus found in the saliva of infected mammals. Travellers can be exposed to it through a bite, scratch or a lick to an open area of skin. Therefore, you should avoid contact with animals, especially wild and stray animals. The vaccination against rabies means that treatment can be given easily and in the country should a risk of rabies occur.
You will require a series of 3 vaccinations to be given over a 3 week period. Or over 1 week if a rapid course is needed. Travellers at greater risk are those who plan to do outdoor activities such as hiking, trekking, cycling or caving.
For more information on our vaccines, please visit our, travel and wellness vaccination pages.
First Aid Kit
For those trekking in the hills, packing good basic first aid kit is essential. The availability of health care and first aid supplies are very limited in rural areas, particularly outside Tirana. Therefore, you should make sure you bring your own adequate basic provisions. These include pain relief, plasters and medication to treat an upset stomach, such as loperamide and oral rehydration salts. Cuts, scapes blisters and even a twisted ankle can occur, so take blister pads, some waterproof dressings and a bandage to deal with any minor injuries whilst you are there.
Access to safe water may be limited. You should consider packing chlorine dioxide tablets to purify your own water. Alternatively, you can purchase a water-to-go bottle which has a built-in filter. If you take regular prescription medication, be sure you pack enough to last your entire journey. And, remember to carry the prescription with you just in case.
Book your travel appointment today
By Anna Chapman | Travel Nurse | September 2019
Bosnia is where East meets West.
It is a country on the Balkan Peninsula in southeastern Europe and has become somewhat a destination for adventurous travellers.
Beautiful Ottoman architecture, rugged mountains, captivating castles, raft-able rivers, and humble hiking trails are all reasons why travellers are choosing Bosnia as their next travel destination. The unveiling of the Via Dinarica mega hiking trail means the number of tourists to the Balkan country of Bosnia Hercegovina is expected to rise steeply. The 1930km trail provides a corridor linking traditional cultures between the former Yugoslavian nations. So whether you plan to mill about the city of Mostar, stroll the streets of Sarajevo, or take a hike in the hillside, ensure you follow our top travel tips to stay healthy.
Vaccinations
All travellers are advised to be in date with their routine immunisations, including diphtheria, tetanus and polio (DTP) and measles, mumps and rubella (MMR). Europe has seen huge outbreaks of measles this year alone, so all travellers should make sure they have received at least two doses of the measles-containing vaccination. A simple blood test can be done for all those who are unsure about their immunity. Some travellers may wish to consider vaccinations for Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B, rabies and tick-borne encephalitis. The activities you plan to do whilst travelling will determine which vaccines would be required. If you have any doubts or concerns, we also suggest booking a pre-travel consultation with a specialist travel nurse to discuss your options.
Find out more about our travel and wellness vaccinations.
Trekking and Ticks
Bosnia offers a wealth of outdoor activities. Those who plan to take advantage of the great outdoors should strongly consider vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis (TBE). TBE is a bacterial infection. Usually, it is spread through an infected tick bite. However, during Spring to Autumn, the consumption of unpasteurised dairy produce also carries a risk. Contracting the illness causes a fever with neurological complications. It is vaccine-preventable. Protection requires 2 doses of the vaccination, given at least 2-weeks apart. A third dose is given 5-12 months later to give longterm protection. You should also avoid ticks by wearing long trousers and socks. Using DEET insect repellant should also repel them.
If you spot a tick on you, it needs to be removed promptly. Use some flat tweezers or a tick remover and clean the bite with alcohol to reduce the risk of infection.
See our Ultimate Bug Kit.
Rabies
Rabies is a fatal virus that can be found in the saliva of an infected mammal. Most commonly a wild dog. Exposure can happen through a bite, scratch or a lick to an open area of the skin. You cannot catch rabies from another person and it cannot spread through unbroken skin. You should, where possible avoid contact with animals when travelling, especially wild or stay animals.
Rabies is almost always fatal once symptoms appear, but treatment before this is very effective. Pre-travel rabies vaccination offers great protection. And means that in the unlikely event you come into contact with the rabies virus, fast and effective treatment can be given easily and in the country of the incident.
Pre-travel rabies protection requires a series of 3 vaccinations given as injections into your upper arm. Your vaccines will be given over a 3-week period, or over 1 week if an accelerated course is needed, prior to travel. Travellers at greater risk are those who plan to do outdoor activities such as hiking, trekking, cycling or caving. You should consider a rabies vaccine if you plan to do any of these activities whilst visiting Bosnia.
First Aid Kit
For those trekking in the hills, packing good basic first aid kit is essential. When travelling in rural areas, access to healthcare can be limited. Travelling with a medical kit will give you access to basic provisions needed to treat minor injuries and pains.
Basic provisions include pain relief, plasters and medication to treat an upset stomach, such as loperamide and oral rehydration salts. If access to safe water may be limited, consider packing chlorine dioxide tablets. Cuts, scapes blisters and even a twisted ankle can occur, so take blister pads, some waterproof dressings and a bandage to deal with any minor injuries whilst you are there. If you take regular prescription medication, ensure you pack enough for the duration of your trip and carry the prescription with you.
Book your travel appointment today
By Anna Chapman | Travel Nurse | August 2019
Japan is hosting the biggest Rugby event of the year in September.
Starting 20th September, across 12 Japanese cities, 48 matches will be played to determine the winner of Rugby World Cup 2019. Millions of people from around the world are expected to travel to Japan to attend this amazing sporting event. Much like any other reason for travelling, it does come with some health risks.
Big sporting events, like the Rugby World Cup, attract huge numbers of people which increases the risk of getting sick and spreading diseases. Venues are sometimes described as giant Petri dishes, where viruses and bacteria can flourish and spread.
But how can you prepare yourself so you remain healthy throughout your holiday?
Be prepared…
Get Vaccinated
It is advised that individuals are up-to-date with routine immunisations including diphtheria, tetanus and polio (DTP).
If you plan to venture outside of the major cities and explore Japan whilst you are there, you may need to consider some travel vaccines, such as Rabies and Hepatitis A or Hepatitis B. If those plans include visiting more rural areas, Japanese Encephalitis could be considered. For those trekking, hiking or camping, a vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis will provide protection against the disease.
MMR is a must
Ensure you are immune to measles before you travel. Japan has had multiple large outbreaks of measles this year and it is a highly contagious disease.
The best protection against measles is to ensure you have received 2 doses of the MMR vaccine. You may not have received the full course during your childhood vaccines which means you’re not fully immune. A simple blood test can determine immunity if you are unsure.
Beware of Flu Season
Flu season for the Northern Hemisphere begins in Autumn, which coincides with the start of the Rugby World Cup. It’s possible people could pick up the flu virus at these events as the Flu is a highly contagious viral disease. Transmission of the flu is always amplified when large groups of people congregate in enclosed space. People travelling to and from mass gatherings can also spread flu to other communities and to family members when they get home. An infected person can transmit the virus before even realising they are sick.
Getting a flu vaccine every year is the best way to avoid getting seasonal flu.
Those travelling from mid-September onwards should consider getting the flu jab as soon as it becomes available.
Find out more about our travel and wellness vaccinations.
Minimize Your Risk
Besides the flu vaccine, here are a few tips on how to minimize your risk of contracting an illness at the Rugby World Cup:
- Keep a distance from people coughing and sneezing – droplets from coughs or sneezes containing flu virus can travel at least 3 feet, so keeping this distance from sick people can help lower your chance of becoming ill.
- Wash your hands often, before eating or after contact with sick people, public places and bathrooms to limit your chances of contact with the virus.
- Carry hand sanitizer to use when hand washing is inconvenient or not available. Ensure it has a minimum of 60% alcohol content to be most effective.
- Avoid touching your mouth, nose and eyes with your hands.
- Use clean, disposable tissues to wipe your mouth or blow your nose. Throw away used tissue immediately after use.
- Avoid getting overly cold and wet by wearing appropriate clothing.
- if you are already sick, wear a face mask to help lower the chance of spreading your illness to others.
First Aid
Despite having a good reputation for health care, it’s worth being prepared for minor illnesses and injuries when travelling abroad. Pack an essential First Aid Kit for your travels and include some basic items such as pain relief, plasters, antiseptic creams and something to treat minor wounds. Being able to treat minor accidents whilst abroad means less time hunting down a pharmacy or time wasted visiting a doctor should you need it.
For convenience, we sell a ready to go Essential First Aid Kit, available online.
You can book a pre-travel consultation online.
Greenland is home to truly magnificent mountainscapes and glaciers.
Jakobshavn Glacier, the world’s fastest-moving glacier in the Northern Hemisphere can be found here.
In the Winter, tourist travel to this wonderland to potentially see the wondrous the Northern Lights. Things are quite different in the Summer.
Chasing the Midnight Sun
Summer in Greenland is an image not often associated with the country. Summertime offers eternal light in the land of ‘The Midnight Sun’ whereby the day has neither a beginning nor an end. Those wanting to experience this time-shifting experience must travel north or the Arctic Circle. The low-lying sun makes the surrounding scenery appear almost dreamlike; icebergs and hilltops are bathed in a surreal palette of pink, purple, yellow and red. Travellers to Greenland have options of hiking the land or sailing the fjords between icebergs.
If you plan to travel to Greenland this summer follow our top travel tips to ensure you stay healthy.
Vaccinations
Even though Greenland resides in the Arctic Circle, travellers should still ensure they receive appropriate pre-travel vaccinations. This includes being up-to-date with Measles, diphtheria-tetanus and polio. Greenland has a high risk of Rabies, a virus spread through the infected bite of a mammal. Travellers who plan to trek inland may wish to consider this vaccination before they travel to reduce the risk.
Suncare
Despite Greenland having long, dark winters, the summer months provide almost constant light. Bright sun, combined with the effects of lights reflection from snow and water can increase the risk of sun damage from UV light. Despite temperatures remaining cold, travellers still need to be sun smart. Ensure you wear a high factor SPF, and use lip balm to prevent cracking. Polarised sunglasses that wrap around will prevent the UV rays causing damage to your eyes.
Sea Sickness
Many activities in Greenland involve taking to the water and visiting the infamous Disko Bay in search of Icebergs. Sometimes the seas can be rough which can make for a miserable time if you are prone to travel sickness.
Sea Sickness can be reduced by:
-
Sit in the centre of the boat where the motion will be less aggressive
-
Close your eyes or focus on a point on the horizon, this can help your inner ear balance.
-
Avoid alcohol and large heavy meals, instead, keep hydrated on water and eat smaller lighter meals
-
Sucking on a mint or ginger sweet can help with nausea
-
Seas Sickness medication tablets
-
Patches that can be used to prevent sea-sickness
Trekking
Parts of Greenland can be remote so taking a good First aid kit with you is essential. Basic provisions include pain relief, plasters and medication to treat an upset stomach, such as loperamide and oral rehydration salts. If you take prescription medication to ensure you pack enough and carry the prescription with you. If you plan on trekking the hinterland, pack additional items such as blister dressings and plasters.
Book your travel appointment today
By Anna Chapman | Travel Nurse | July 2019
The Southern African nation, Mozambique is gaining popularity amongst the adventure traveller community. Often referred to as ‘The Pearl of the Indian Ocean’, it is well off the usual tourist trail of Africa. Mozambique offers rustic beaches, delightful architecture, superb national parks, and plenty of diving opportunities.
Many choose to start their adventure exploring the capital city, Maputo. It is easy to understand why. It is rich in culture with beautifully preserved Portuguese colonial architecture. You could easily spend a week enjoying the hospitality of the friendly locals, eating the delicious food and partying the night away. Maputo is a largely-underestimated African capital city.
Mozambique is also known for having some of the most pristine dive sites in the world. Tofo is arguably one of the greatest places on Earth to see megafauna marine life. Crystal clear water provides perfect visibility to view the abundant marine life. The beautiful tropical Islands of the Bazaruto and Quirimbas Archipelagos are some of the most romantic and secluded beach destinations in the world – ideal for honeymooners.
Whatever your holiday entails, ensure you read out top travel tips to stay healthy in Mozambique.
Vaccinations
Travellers should ensure they are up-to-date with their routine immunisations including measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) and diphtheria-tetanus and polio (DTP). Additional travel vaccinations are advised including hepatitis A, typhoid, rabies and hepatitis B. It’s best to speak with a travel nurse about any specific travel vaccinations you may need in a pre-travel consultation.
For more information on our vaccines, please visit our, travel and wellness vaccination pages.
…What about Yellow Fever?
Yellow Fever is a viral haemorrhagic illness spread from the infected bite of the Aedes mosquito. Whilst it can occur in parts of Africa, there is no risk of Yellow Fever in Mozambique. Therefore, travellers do not need to be vaccinated.
The only exception to this will be for travellers who are entering Mozambique from a country which does have a risk of the illness. In this case, it is best to speak to a travel nurse to see if you require the vaccine. If you do, you will need to be in possession of a Yellow Fever Vaccination certificate as a condition of entry. Ask your travel health specialist for advice.
…And Polio?
Polio is a viral infection. As it is contagious, you can get polio from contact with an infected person. In addition, consuming food or water that has been contaminated by a person with poliovirus also puts you at risk. There has been a worldwide effort to eliminate polio, which is proving highly successful. However, Mozambique still remains at risk due to vaccinate-derived circulating strains. All travellers should ensure they are up-to-date with their polio immunisation. The polio vaccine is a combination vaccination, given with diphtheria and tetanus. It provides protection for 10 years.
If you plan to stay for longer than 4 consecutive weeks, it’s advised that your polio vaccine be administered within the last 12-months. You should also have the dose recorded on an International certificate of vaccination prophylaxis card as proof of immunisation. Furthermore, long-term travellers to Mozambique may be required to show this when they leave the country, as proof they have been immunised.
Malaria
All of Mozambique has a risk of malaria. Malaria is an infection spread by the Anopheles mosquitoes which are most active during dusk till dawn. You should take strict precautions against mosquito bites. This includes wearing long loose clothing and using an insect repellent with a minimum of 50% DEET. You can reduce the risk of indoor mosquito activity with the use of plug-in vaporisers. Plus, sleeping under a mosquito net can help reduce night-time bites.
We recommend taking antimalarial medication for the duration of your trip. As there are different options available, it’s best to speak to a travel nurse to find the best option for you and your family.
See our Ultimate Bug Kit.
Special precautions post-Cyclone Idai
Cyclone Idai battered the coast of Mozambique on the 9th March 2019. The storms brought heavy rains, winds and flooding. As a result of the initial impact alone, there were hundreds of fatalities. The storm created many serious health risks. Firstly, like most natural disasters, the storm has displaced a huge number of local people. Which as a result, will increase the risk of diseases spreading. Secondly, it has placed a strain on the countries structural and health infrastructure. Which as a result, and can lead to further flooding and increases the risk of water-borne infections such as cholera. Thirdly, the increase of water has led to an increase in breeding sites for mosquitoes. Therefore, there is an increased risk of malaria and other mosquito-transferred diseases.
Although the risk for tourists will be much lower than that of the local population, extra precautions to avoid infectious diseases should be taken. You should pay extra attention to the food and water hygiene you consume. This will minimise the risk of you getting a diarrhoeal illness.
If you are travelling to an area with a known outbreak, the Cholera vaccine can be considered. Similarly, those undertaking humanitarian work or those with inadequate access to safe water and sanitation should also consider the vaccine.
Book your travel appointment today
By Anna Chapman | Travel Nurse | July 2019
A safari in Namibia is a unique experience in Africa. It has the highest sand dunes on the continent, the world’s oldest and uninhabited deserts, the Skeleton Coast and a lush jungle to the north. Whatever you have planned on your trip, ensure you follow our top travel tips to stay healthy.
Vaccines
All travellers need to ensure they are up-to-date with Hepatitis A, Typhoid and Diphtheria, Tetanus and Polio (DTP). These are your basic traveller vaccine requirements. You may wish to consider further vaccinations against Rabies and Hepatitis B.
There is no risk of Yellow Fever in Namibia, however, travellers who will arrive in Namibia having transited from a country with a risk of Yellow Fever will be required to be in possession of a valid Yellow Fever Certificate.
Countries this would apply to include Kenya, Nigeria, Zambia, Ethiopia, Brazil, Peru and Bolivia. For the full list of countries with risk of yellow fever transmission as per the World Health Organisation.
For more information on our vaccines, please visit our travel and wellness vaccination pages.
Malaria
There is a risk of malaria in the northern areas of Namibia of the Kunene River, Caprivi and Kavango regions and Etosha National Park. Windhoek, Swakopmund and the Skeleton coast have a low risk of malaria. If you intend to visit malarial regions, ensure that you take the antimalarial medication with you. Mosquitoes that are responsible for the spread of malaria are most active between dusk and dawn, and therefore you need to be extra cautious during this time against mosquito bites.
Insects
Ticks, flies and mosquitoes all have the ability to transmit unpleasant disease in Namibia. The best prevention against these diseases is to avoid mosquito bites. Cover up as much as possible and apply a minimum concentration of 50% DEET to any areas of exposed skin. Clothes can be treated with permethrin before setting off to provide an extra level of protection. Sleep under a mosquito net especially if you plan to stay anywhere remote or rural.
See our Ultimate Bug Kit.
Food and water
Travellers should exercise caution with food and water when travelling to Namibia to avoid tummy troubles. Do not drink tap water in Namibia, stick to bottled water or water that has been boiled. If you are undertaking a self-drive trip and plan camping in remote areas it is a good idea to take either a water bottle with a filter or some chlorine dioxide tablets to make water safe to drink should you not be able to find a shop with bottled water. The Namib Desert is one of the aridest in the world so always ensure you pack extra water.
See our Worldwide Gastro Kit to help with any travellers tummy troubles.
Book your travel appointment online today.
By Anna Chapman | Travel Nurse | June 2019
Travel nurse Anna takes us on a journey to Tel Aviv. A city on Israel’s Mediterranean coast steeped in history and a vibrant cultural scene. From vaccinations to sun protection follow the top tips to travel safely.
Vaccines
All travellers are advised to ensure that they are in date with their routine vaccinations. Measles outbreaks have been reported in Israel since September 2018, and there are concerns that the increase of travellers heading to Israel for Passover in mid-April could see cases rise. Travellers should ensure that they have received two doses of measles vaccination (often referred to as the MMR) prior to departure.
Other travel vaccinations to be considered are diphtheria, tetanus and polio, and Hepatitis A. Some travellers may also wish to consider vaccinations against Hepatitis B and Rabies. It is always best to discuss which vaccinations are necessary for your trip with a travel nurse.
However, vaccinations cannot protect you from many diseases and dangers in Israel, the risk can be reduced through your behaviours…
Sun
Israel lies within the sub-tropical region with a Mediterranean climate. Summer temperatures can reach 40 degrees Celsius, and even higher in the Negev desert. Don’t let the Mediterranean summer breezes deceive you and stay sun safe. Keep hydrated, wear a high factor sunscreen and avoid the suns rays between 11am-3pm when at its strongest.
Food and Water
Israel is foodie heaven but travellers should still maintain good food and water practices to avoid tummy trouble whilst away. Avoid tap water and ice made from tap water: stick to bottled water. Ensure you wash your hands thoroughly before eating and after using the toilet. Ensure all food you eat is cooked thoroughly and served straight to you. For those who would still like the freedom to eat and drink without worry, it is advisable to carry a gastro kit with you. Inside will be various medications that can assist with travellers’ diarrhoea, should it occur.
Insects
Mosquitoes and sand flies can be particularly problematic during the summer months. Not only can their bites cause irritation, but they can also spread diseases such as West Nile Fever, dengue fever and leishmaniasis. There are no specific vaccinations and preventative treatments for these diseases, and bite avoidance is the only way. Try and cover up especially between dusk and dawn, and wear a good insect repellant that contains at least 50% DEET.
See our Ultimate Bug Kit.
From Red to Dead…
From the riches of the coral seas in the red to the abyss of the dead sea, take sensible precautions when taking the plunge. The dead sea lies 413m below sea level and is actually rather tricky to swim in. Tourist usually come to float on its surface as the high salt content makes it hard to submerge. Be careful. Cover any cuts you have with waterproof plasters to avoid a sharp sting. Do not splash when in the water, as it may cause injury or irritation to your eye if it enters. If you wear contact lenses, it’s best to swap to your glasses.
You can book all vaccination appointments or travel consultations online.
By Anna Chapman | Travel Nurse | May 2019
Sepsis Signs:
World Sepsis Day – 13 September
Sepsis is a global health crisis and affects 27 to 30 million people every year. Out of those affected, 7 to 9 million dies. That’s one death every 3.5 seconds.
Sometimes called the silent killer, Sepsis is a bacterial infection of the blood which can become life-threatening. It is very hard to detect in the early stages, with symptoms similar to many other conditions and illnesses. In the UK alone, around 37,000 people die from sepsis each year.
Thankfully, due to public awareness increasing due to medical bodies and health campaigns, sepsis is being talked about more. As a result, parents and doctors have the condition forefront-of-their mind. The condition is treatable with early recognition and care.
Causes of Sepsis
Bacterial infections are the most common causes of Sepsis. However, Sepsis can also be caused by infections like seasonal influenza viruses, dengue viruses, and highly transmissible pathogens.
Children under 1, the elderly and those with chronic diseases and a weakened immune system are most at risk of sepsis.
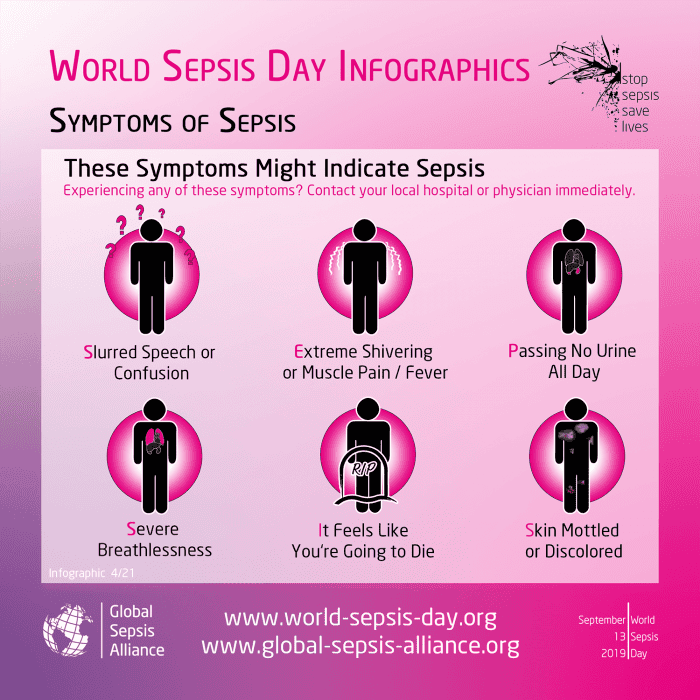
Symptoms of Sepsis
Sepsis can display in a variety of ways including:
-
Slurred speech or confusion
-
Extreme shivering or muscle pain or fever
-
Passing no urine all-day
-
Severe breathlessness
-
It feels like you’re going to die
-
Skin mottled or discoloured
If someone is ill and is getting progressively worse with two or more of the above symptoms, then it is advised for you to go to A & E without delay.
Preventing Sepsis
Preventing infection in the first place is the best way to prevent Sepsis from occurring.
This can be done by:
- Vaccinations – protect yourself from diseases which if serious, could lead to Sepsis.
- Hand Hygiene – reduce the spread of diseases and infections.
- Safe Childbirth – reducing infection to the mother and baby.
- Awareness of Sepsis– knowing the causes and symptoms can save lives.
If you think you are experiencing symptoms of sepsis, you should call 111 as you may require immediate medial attention.
For general GP health checks or vaccinations, you can book an appointment online.
Ask the average person what viral disease they think claims the most lives, and HIV might be the likely response. However, this is not so, according to research in the Lancet. The research suggests that viral hepatitis caused 1.45m deaths in 2013 compared to 1.2m lives claimed by AIDS in 2014. What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is best defined as an inflammation of the liver caused by the hepatitis virus. There are 5 types of hepatitis virus called; A,B,C,D and E. Contaminated food is usually the cause of virus types A and E. Types B, C and D are spread via infected bodily fluid contact. Virus types B and C lead to the most deaths.
Prevention
Hepatitis A and B are vaccine preventable. Many countries offer these vaccines routinely on the childhood schedule but this is not the case in the UK.
Hepatitis Vaccination at the Fleet Street Clinic
Vaccinations are needed to give protection against hepatitis A and B and they currently are not part of the childhood vaccination schedule in the UK. At the Fleet Street Clinic, we make it a priority to have a good supply of hepatitis A and B vaccines for children all year round. The hepatitis vaccinations can be given individually, or as a combined injection. For long lasting protection, several doses are required. Our vaccination team are highly trained, well-qualified and have dozens of years’ experience between them. Our vaccination service takes place in a clean, comfortable and safe environment.
You can learn more about our vaccinations here.
While hepatitis is causing millions of fatalities across the globe, you can take steps towards protection against the virus by booking an appointment for hepatitis vaccinations at Fleet Street Clinic today.
Boating in the Bahamas
The best way to see the Bahamas is by boat. As an archipelago of over 700 islands and cays all strung together like pearls over a turquoise sea, the majority of visitors choose to cruise to see the many delights that this country has to offer. Whether you only visit the Bahamas or take an all-encompassing Caribbean cruise, it is important to remember those travel vaccinations and travel health advice are essential if you are to enjoy a happy healthy holiday.
Here are our top travel tips for staying healthy in the Bahamas…
Vaccinations
All travellers should be in date with diphtheria, tetanus polio and Hepatitis A. There is no risk of the Yellow Fever virus in the Bahamas, however, if your cruise takes you to an area that does have a risk of the virus (such as South America), you will need to provide evidence of vaccination in the form of a valid Yellow Fever certificate. Cruise ships are confined spaces with a high volume of passengers which makes you more susceptible to infections. If you plan on travelling during the winter months, it is sensible to consider a flu vaccination as respiratory viruses can spread easily.
Sun
The Bahamas lie in the tropical Caribbean seas making the sun, sea and sand the major attraction. Remember to be sun safe. Wear a high factor sun cream throughout your holiday. The sun’s rays are particularly strong between 11am-3pm so it’s best to avoid direct exposure during this time. Slap on a hat, slip on a shirt and slop on some sunscreen.
Insects
The Bahamas have a risk of dengue fever, chikungunya and the Zika virus. These illness are spread via the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito. Whilst causing mild illness in many, they can cause more serious complications and are best avoided. Zika virus is associated with a serious complication during pregnancy and those who are pregnant or plan to become pregnant soon after the trip are advised against travel to the area. There are no specific vaccinations against these mosquito-borne viruses so bite prevention is the only defence. Cover up exposed skin and wear an insect repellent containing at least 50% DEET.
See our Ultimate Bug Kit.
Gastro Kit
The majority of Bahamian cuisine comes straight out of the sea. Whilst seafood and fish are delicious, ensure that any food consumed is cooked thoroughly and served fresh to you. The Bahamas has an abundance of fresh tropical fruit but it is wise to adhere to the ‘cook it, boil it, peel it or forget it’ saying to avoid the dreaded traveller’s diarrhoea. We advise travellers to take a gastro kit with them which can help prevent and treat the commonest gastrointestinal symptoms that occur when travelling.
Cruise Health
If you do plan to see the Bahamas by boat, ensure you follow some sensible precautions to avoid getting sick from fellow passengers. Wash your hands regularly, make use of the alcohol-based sanitizers stations on board, carry a small alcohol-based hand sanitiser to keep your hands clean when off the ship. Ensure you stay hydrated, but make sure you drink water from a safe source (bottled, boiled or purified).
Book your travel appointment today
By Anna Chapman | Travel Nurse | March 2019
At present, there is currently a shortage of Hepatitis B vaccine available in the United Kingdom and across the world.
Despite current global shortages, Fleet Street Clinic maintains good stock levels of the Hepatitis B vaccine.
The Hepatitis B virus is one of the most prevalent blood-borne viruses worldwide and is a major cause of chronic liver disease and liver cancer. In the majority of cases, Hepatitis B is asymptomatic – without symptoms. It is easily preventable through vaccination, and we strongly believe this vaccine should be offered more widely – all young, sexually active adults ought to be protected.
Although the overall risk for travellers is low, Hepatitis B immunisation is recommended for travellers travelling to East Asia and Sub Saharan Africa where between 5 – 10 % of the adult population is estimated to have persistent Hepatitis B infection. High rates of infection are also found in the Amazon, southern parts of eastern and central Europe, the Middle East and Indian subcontinents. The risk understandable increases for long-stay travellers in high-risk areas.
Certain behaviours and activities put individuals at higher risk, such as unprotected sex, adventure sports, body piercing, tattoos and injected drug usage.
Receiving medical or dental care in high-risk countries will also increase your risk and it is advised to avoid unless absolutely necessary. Travellers who have pre-existing conditions which may make it more likely for them to need medical attention should definitely consider the Hepatitis vaccination prior to travelling.
Some viruses thrive in the winter and are easily spread during cold weather. The lack of sunlight also means there is less Vitamin D in your body during winter, which can lower your immune system. This makes it harder for the body to fight off infections, resulting in a higher chance of sickness, even amongst the healthy.
If you’re planning on avoiding the flu this year, going on holiday, starting University, having a child or just living a healthy lifestyle in general, then there are a number of extremely important vaccines you should know about.
1. Flu Vaccine:
Now is the perfect time to have your flu jab, to ensure protection for the entire winter. Our adult flu vaccines are already in stock including Quadrivalent, FluAd and egg-free. Due to distribution delays, needle-free Quadrivalent vaccines for kids will be arriving soon.
– Find out more about the Flu Vaccine
2. MMR – Measles, Mumps and Rubella:
Many people who are now adults have never been vaccinated against measles, mumps or rubella, either from concerns over misinformation during the 1990s or because they simply missed out on getting protected. As a result, there has been an alarming rise in cases and outbreaks, with several deaths. Unfortunately, this year the UK also lost its ‘Measles Free’ status. Two doses are needed for protection, and it is never too late to be vaccinated!
– Find out more about the MMR Vaccine
3. Chickenpox:
There’s no need for any child to go through the misery of the chickenpox. It is entirely preventable with a vaccine that is still not yet available on the NHS, Varicella. This vaccine can be given to children over the age of one year. 2 doses are recommended for full protection.
– Find out more about the Chickenpox Vaccine
4. Shingles:
Shingles is a horrible reactivation of the chickenpox virus in adults who have had chickenpox during childhood. It consists of a painful, blistering rash. The pain can linger for months or years but it is also preventable. Shingrix is a relatively new vaccine which provides the best protection against Shingles. It offers up to 90% immunity. Supplies worldwide are limited but The Fleet Street Clinic is one of the first medical practices in the UK to make it consistently available.
– Find out more about the Shingles Vaccine, Shingrix
5. HPV (Human Papilloma Virus) Vaccine:
HPV is the leading cause of cervical cancer but also causes other genital, head & neck cancers. The national programme offers all 12- and 13-year-olds in school the Gardasil HPV vaccine. HPV-4 protects against 4 types of HPV. There is no “catch-up” programme for older children and adolescents.
At Fleet Street Clinic, we offer Gardasil 9. It offers greater protection against 5 additional types of HPV. In our opinion, if you have not received the HPV vaccine yet, you are better to get the HPV- Gardasil 9 vaccine to benefit from the extra protection it offers.
– Find out more about the HPV Vaccine, Gardasil 9
6. Whooping Cough:
Childhood vaccination does not give lifelong protection, and newborns are especially vulnerable. Vaccination is recommended during pregnancy, and may also be advisable if you have a close family member who is pregnant, or if you’re likely to be in close contact with their newborn baby.
– Find out more about Whooping Cough
7. Meningitis:
We offer Meningitis ACWY and Meningitis B vaccines. This vaccine is recommended to all those who fall outside the age groups currently targeted by the NHS or have an important deadline for protection.
– Find out more about Meningitis ACWY and Meningitis B vaccines
8. Hepatitis B:
Hepatitis B is spread by blood and body fluids. In most other developed countries, it has been a standard part of the childhood vaccination schedule for many years, but in the UK it has only just been added to the schedule at birth and infancy. There is no “catch-up” programme for older children and adolescents. We strongly believe this vaccine should be offered more widely – all young, sexually active adults ought to be protected.
– Find out more about Hepatitis B
9. Pneumonia:
We strongly recommend the Prevenar pneumonia vaccine for those aged 65 and over. Pneumonia can affect people of any age, but it’s more common and can be more serious, in certain groups of people, such as the very young or the elderly. Anyone with a past history of pneumonia, asthma or lung disease should also consider this vaccine. Anyone can get a pneumococcal infection, but not everyone is offered the pneumococcal vaccine on the NHS. Prevenar pneumonia vaccine protects against 13 of the most common strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria.
– Find out more about the Pneumonia Vaccine
10. Rabies:
At the Fleet Street Clinic, we are well known for offering the full range of travel vaccines, always in stock. But if I had to pick just one vaccine I would never want to be without, it would be rabies. Protection is cheap, easy, safe and long-lasting – but expensive and hard to find if you are ever unlucky enough to be bitten abroad. I was once attacked by a dog in a remote part of Peru, and have had to look after dozens of travellers who have been in similar situations.
– Find out more about the Rabies Vaccine
Get in touch…
If you would like more information or require any of these vaccinations, please give us a call to arrange an appointment or book your appointment online today
Anna Chapman, one of our experienced Travel Nurses, gives her top 5 reasons why having a travel consultation is so important … food for thought if you’re planning a trip abroad.
1 – Reputable advice from a trusted source
Clinics that specialise in travel have practitioners who have completed extra qualifications in travel medicine, such as a Diploma in Travel Medicine, Diploma in Tropical Medicine and Certificate of Travel Health. These qualifications ensure the practitioner gets specialist knowledge that is kept up-to-date by attending conferences and participating in research in the field. Many practitioners who work in travel medicine have experienced health care abroad, through extensive personal travel or through working or volunteering. This means the travel advice that a patient receives is always current and accurate.
Our travel nurses at the Fleet Street Clinic have a Diploma in Tropical Nursing and a Certificate in Travel Health and both GPs have a Diploma in Travel Medicine and a Certificate in Travel Health. All the practitioners in our Travel Clinic have travelled extensively and practiced their profession in developing countries. This means they are more aware of the risks that travellers face and have a greater understanding of how to deal with health issues on the road.
2 – Personalised travel consultation
No two people are the same and no two travel itineraries are the same. Travel consultations take this into account and give detailed and bespoke travel advice, not only for the itinerary but also for the individual. Seeing a practitioner face-to-face means that personal risks can be evaluated to ensure all travel health needs are met, rather taking a “one size fits all” approach.
3 – Travel health is NOT just about travel vaccinations
Whilst vaccinations are important, there are many aspects to staying healthy while abroad. In addition to vaccinations, there are considerations such as avoiding insect bites, use of medical kits, coping with jet lag, use of stand-by medications and coping with altitude sickness – all things that can be discussed when you have a travel consultation
4 – On-going care
Just because you have had your vaccinations before your trip, it doesn’t mean that your care ends when you leave the clinic. Specialist clinics can provide on-going care for subsequent trips and/or post-travel health concerns
5 – Time to talk
When a clinic has a specialist travel service, ample time is allocated to each appointment. Having a team of dedicated staff committed to travel medicine means that appointments can be completely flexible and can accommodate individuals, groups or families, both at the clinic or off-site, as well as offering appointments for last minute travellers.
You can book a travel health consultation online. Or see here, or more information about our travel health services.