Tag: Dengue Fever
Dengue has been declared an epidemic in the state of Karnataka in India.
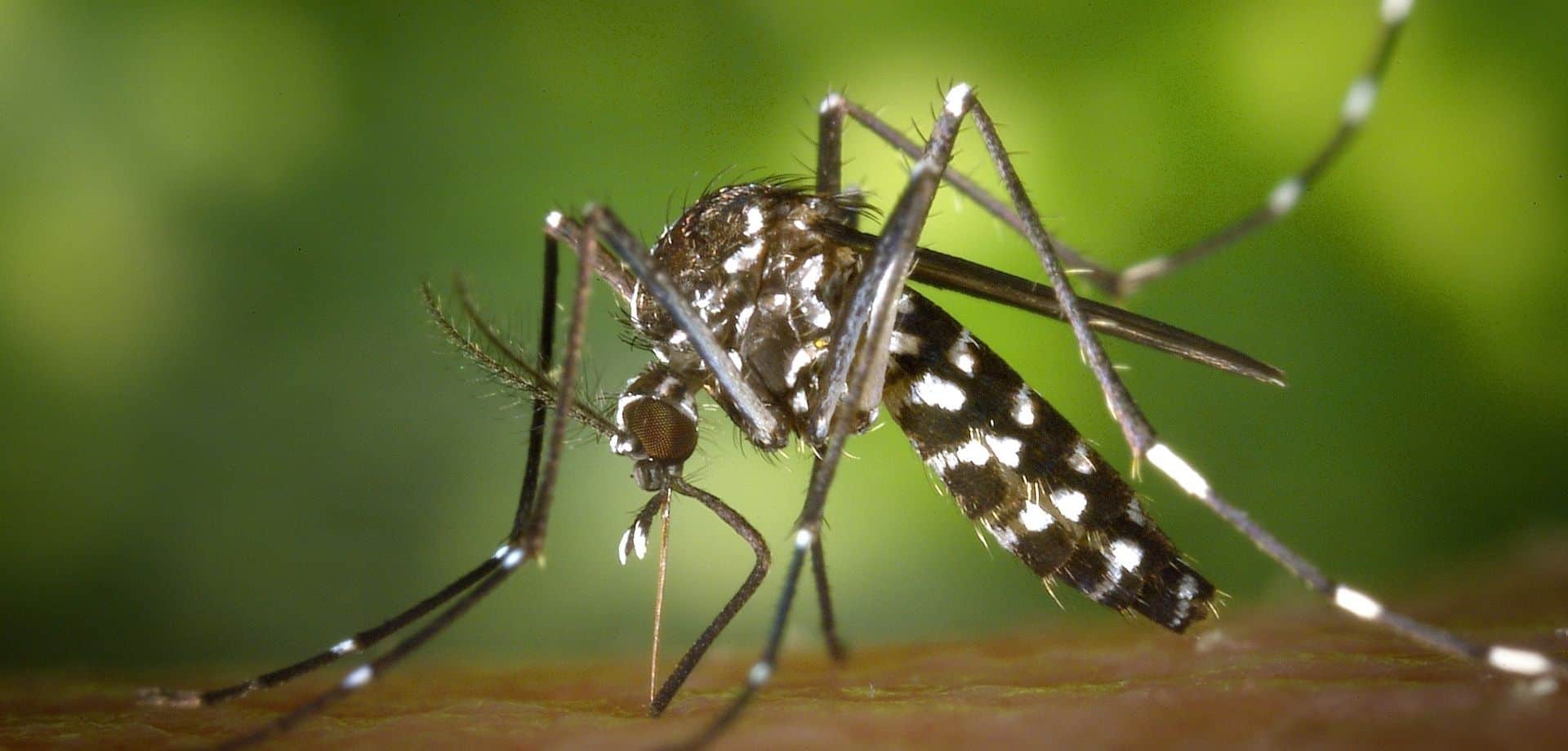
Dengue fever is an unpleasant viral infection spread by the bites from infected Aedes mosquitoes. Unlike the mosquitoes that transmit malaria and are active at dusk, Aedes mosquitoes are most active during daylight hours, making dengue prevention more challenging.
As of this week, Karnataka has reported 25,589 cases and 12 deaths so far, with a staggering 15,000 new cases in the last 45 days alone—the highest in a decade.
Bengaluru, one of the hardest-hit cities, has recorded over 11,500 cases, driven by the rainy season that has created ideal mosquito breeding conditions.
To combat this, the government is enforcing strict measures, including penalties for property owners who allow mosquito breeding. However, personal protection remains critical, especially for those planning to travel to India.
At Fleet Street Clinic, we offer Qdenga®, the newest dengue vaccine. As a live vaccine, it’s not suitable for everyone, so we recommend booking a consultation with one of our specialist travel nurses to determine if it’s right for you.
Safety Tips:
In addition to vaccination, follow these safety tips:
- Cover up, wear long sleeves and trousers when there are mosquitoes around.
- Use mosquito repellent creams, coils, and sprays.
- Use a mosquito net at night
- If you experience symptoms like fever, muscle aches, nausea, or vomiting, seek medical attention.
If you’re planning to travel, ensuring your vaccinations are up-to-date is essential for your safety. To determine if the Qdenga® vaccine is right for you, we recommend booking an online consultation with one of our expert travel nurses.
The Qdenga® vaccine requires two doses, with each dose priced at £148. Our specialists will provide personalised advice and help you navigate your vaccination needs.
Click to book your appointment.
For more information on:
Dengue Epidemic in Karnataka, India
Karnataka declares Dengue an Epidemic
In the months since its release in the UK, we have seen a huge demand for the new Dengue vaccine, Qdenga.
For those with experience of the disease, the news of its licensing has been much anticipated and we are proud to be one of the first clinics in the UK to offer the vaccine.
What is Dengue Fever?
Dengue is a viral infection that is spread through the bite of an infected aedes mosquito, a species easily recognisable by its striped legs. It occurs in over 120 countries worldwide, mainly in the tropics and sub-tropics, and is the second most common cause of fever in the returning traveller.
The most seriously impacted regions are the Americas, South-East Asia, and Western Pacific, with Asia accounting for around 70% of the world’s disease burden.
It is also spreading to new areas, including Europe, where outbreaks have been increasing in recent years. Read more about this in our recent blog, Dengue Fever in Europe: Temperature Risk.
Since it is transmitted from person to person, via the mosquito vector, it is of particular concern in populated, urban areas.
What are the symptoms of Dengue Fever?
Whilst most cases are asymptomatic, some will develop a severe flu like illness that can require hospitalisation. In rare cases, this will be life threatening.
Common symptoms include;
a high fever,
severe headache,
pain behind the eyes,
muscle ache,
joint pains,
nausea,
vomiting and rash.
There are four serotypes of Dengue virus; for those infected by one type, a subsequent infection is more likely to be life threatening. The severe type of Dengue usually starts a few days after the initial symptoms began. After feeling a bit better, symptoms suddenly return and can include severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting and bleeding.
Approximately 1 in 20 patients with Dengue will progress into the severe form of the disease.
Dengue Fever Vaccination
Historically, the only protection we could provide was advice surrounding mosquito bite avoidance. With the arrival of Qdenga, we now have the option of a vaccination which provides safe and effective protection.
Studies have shown Qdenga to offer 80% protection from the first dose, with long term immunity achieved after the second.
Who should get vaccinated?
Qdenga can be safely given to those who have previously had the disease, and it is especially important for this group. We would also encourage frequent or long stay travellers to consider the vaccine. The vaccine is licensed for the prevention of Dengue in individuals from 4 years of age and requires two doses, to be given three months apart.
It is a live vaccine, so it’s not suitable for everyone. To discuss your suitability with one of our specialist travel nurses, please book a travel consultation online, or call our reception team on +44 20 7353 5678.
We can usually accommodate same day bookings and suitable vaccinations can be given within the same appointment.
Related services available at Fleet Street Clinic
Travellers’ Diarrhoea Online Consultation
For further reading
Dengue Fever has been in the news following two cases linked to travel to the Spanish island of Ibiza. This has sparked concerns about the spread of mosquito-borne illnesses in Europe, which is especially unusual for this time of year.
Dengue fever is a viral infection transmitted by the Aedes mosquito, which is found in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. With rising temperatures and changing climates, there is a risk of mosquitoes and other disease vectors spreading to new areas, potentially causing outbreaks of diseases such as dengue fever.
The two cases of dengue fever in Ibiza were reported by the Spanish Ministry of Health and were both in residents of Germany who had visited the island before becoming ill. Each case was accompanied by two family members who were also suspected to have had dengue fever.
The risk of dengue fever in Spain is highest between the months of May and November, when mosquitoes are most active so to have cases at this time of year is uncommon.
So, why are we seeing cases outside of the usual infection months?
The reason is multi-facetted.
Our medical director and travel health specialist, Dr Richard Dawood explains:
“Firstly, there is the introduction or spread of mosquitoes to “pastures new” – places that might have been previously inhospitable, perhaps through temperature; or alternatively, that offer an environment with plenty of suitable breeding sites that they are suddenly able to take advantage of. These mosquitoes can bring disease with them, or can spread it around if there is a reservoir in the local population.
Secondly, there is the possibility of introducing disease to a vector population that is already established, ready and waiting. This is exactly the (long-standing) concern with yellow fever. There are mosquito species in Asia, for example, that are easily capable of spreading yellow fever were it to be introduced by an infected traveller – which is why Asian countries are so careful to insist on proof of yellow fever vaccination from travellers arriving from the endemic zones of Africa and South America. Asia is yellow fever-free, and wants to remain so. However, this type of introduction has already recently happened in Australia, where Japanese encephalitis (a virus infection that can cause rare but serious complications in humans) has recently established a reservoir of infection in farm animals, that may be impossible to reverse. It is also happening with Lyme disease spreading gradually into parts of Europe (and the UK) with a susceptible tick population.
Similar concerns apply to Zika – there is very large potentially susceptible mosquito population that could spread the virus in many tropical countries, if introduced; dengue fever; and also potentially malaria, in parts of the world that have been the target of successful elimination campaigns, but where mosquito populations could still spread it, were it to be reintroduced, if control measures are neglected or ceased.
With changing climates, a valid concern about global warming is that it could create conditions in which populations of mosquitoes and other vectors thrive and spread – hence the crucial importance of vigilance, surveillance, and early action if needed.”
How can you protect yourself from Dengue Fever?
QDENGA, Dengue Fever Vaccination
Relatively new to the UK, QDenga is a new travel vaccine that can prevent dengue fever.
The course consists of two doses, given three months apart, and provides long lasting protection.
Learn more about QDENGA, Dengue Fever Vaccination
Book a travel consultation for your Qdenga vaccination.
Avoid Mosquito Bites
In addition to vaccination, the best way to protect yourself against dengue fever is to take measures to avoid mosquito bites. This includes wearing protective clothing, using mosquito repellent, and staying in places with air conditioning or screens on windows and doors.
If you develop a high fever during or after travelling to an affected area, seek medical advice as soon as possible and provide details of your recent travel history. Dengue is often also accompanied by a rash and joint or muscle pain.
In conclusion, rising temperatures and changing climates have the potential to create conditions in which populations of mosquitoes and other disease vectors thrive and spread. It is crucial for public health authorities to remain vigilant and take early action if needed to prevent the spread of diseases such as dengue fever.
By receiving the Qdenga vaccine and implementing effective measures to prevent mosquito bites, travellers can lower their personal risk of contracting Dengue Fever, along with other insect-borne diseases.
If you’re considering Qdenga before your next trip, book a travel consultation with one of our specialist travel nurses.
Related services available at Fleet Street Clinic
QDENGA, Dengue Fever Vaccination
Suitable Medical Kits available to buy online
Related Online Consultations
Female Travel Health Kit: Start Consultation
Have a bug-free beach life
Apart from causing an itch and inflammation, mosquitoes can leave more than just an irritation.
In the Caribbean, they have the ability to transmit diseases such as Dengue Fever, Zika Virus and Chikungunya.
Mosquito bite avoidance is recommended, here are our recommendations on how:
- Cover up with clothing
- Use insect repellents containing a minimum of 50% DEET on any exposed skin
- Consider treating clothes with permethrin
- Sleep under bed nets and use insect screens on doors.
- Reduce mosquito breeding sites by removing any water containers from outdoor areas
- Use air-conditioning
- Consider the use of plug-in electrical vaporisers which deter mosquitoes
- Use our Ultimate Bug Kit.
Dengue Fever & Chikungunya
There is currently no vaccine available to prevent either dengue nor chikungunya in travellers. However, without mosquitoes, individual sufferers are not directly contagious.
The risk for both diseases is thought to be higher during periods of intense mosquito feeding activity (two to three hours after dawn and during the early evening).
Zika
There is currently no vaccine available to prevent the ZIKV infection in travellers. Those infected with the infection normally have no symptoms. When symptoms do occur they are usually mild and short-lived. Serious complications and deaths are not common.
The concerns with the Zika virus and primarily to do with birth defects and as a result pregnant women should postpone non-essential travel until after pregnancy. More information on Zika Virus and pregnancy concerns from Public Health England.
So say ‘zip off’ to zika and ‘do one’ dengue and enjoy a bug-free beach life!
If you would like more travel advice we’d recommend an appointment with one of our travel nurses. You can book your travel appointment online.
By Anna Chapman | Travel Nurse | November 2018
The popular Thai tourist resorts of Krabi and Phuket are reporting high incidences of dengue fever this year.
Since January 2015 over 400 cases of dengue fever have been reported, resulting in one fatality.
Cases of dengue fever also soared in Malaysia with over 40,000 reported cases this year. It is estimated between 6-10 cases of dengue are diagnosed each day – double the rate of last year. The most dramatic increases have been seen in Penang, Johor and the state of Selangor.
Dengue Fever Advice for Travellers
Unfortunately, there is no vaccine or medication that can prevent dengue. The only way to reduce the risk is to prevent mosquito bites, particularly during daylight hours.
If you are off on an Asian adventure this summer, follow these simple steps to reduce the risk of dengue fever:
- Cover up with clothing
- Use insect repellents containing a minimum of 50% DEET on any exposed skin
- Consider treating clothes with permethrin
- Sleep under bed nets and use insect screens on doors.
- Reduce mosquito breeding sites by removing any water containers from outdoor areas
- Use air-conditioning
- Consider the use of plug-in electrical vaporisers which deter mosquitoes
Our Ultimate Bug Kit contains everything you need to help keep mosquitos at bay and is available to purchase online.
Fleet Street Clinic
For more information on Dengue or any other travel-related topic, you can book travel consultation appointment online.