Tag: GP advice
Statins are a widely prescribed class of drugs used to lower cholesterol levels and prevent cardiovascular events such as heart disease and strokes. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has recently released updated guidelines on the use of statins, which now recommend that they can be considered for people at a lower risk threshold.
This decision was made after the independent committee updating the NICE guideline on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk assessment and reduction considered new evidence on the safety and side effects of statins, meaning more people could be given them.
The draft guideline recommends that doctors should consider statins for people who haven’t had a CVD event (called ‘primary prevention’) with a 10-year CVD risk score of less than 10%. The committee agreed that if more people took statins there would be a greater reduction in the incidence of heart disease and strokes.
In addition to being prescribed by National Health Service GP’s, statins can also be prescribed by private healthcare providers, such as us, Fleet Street Clinic. In fact, private GP’s can play an important role in the management of cardiovascular disease risk by offering statins as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for patients at high risk.
People can be at risk from CVD because of factors they cannot change including their age, sex, ethnicity and family history but it’s important to note that certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk. These include stopping smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, introducing or increasing exercise and eating a healthy diet.
Therefore, the decision to take a statin should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional and should take into account the individual’s values and priorities as well as the potential risks and benefits of treatment.
With the British Heart Foundation noting that “there are around 7.6 million people living with heart and circulatory diseases in the UK” and that they “estimate that in the UK more than half of us will get a heart or circulatory condition in our lifetime” this is likely to be an impactful change in the landscape of CVD and statins.
To conclude, Paul Chrisp, director of the Centre for Guidelines at NICE, said:
“What we’re saying is that, for people with a less than 10% risk over 10 years of a first heart attack or stroke, the decision to take a statin should be left to individual patients after an informed discussion of benefits and risks.
“The evidence is clear, in our view, that for people with a risk of 10% or less over 10 years, statins are an appropriate choice to reduce that risk.
“We are not advocating that statins are used alone. The draft guideline continues to say that it is only if lifestyle changes on their own are not sufficient, and that other risk factors such as hypertension are also managed, that people who are still at risk can be offered the opportunity to use a statin, if they want to. They don’t have to, and their decision should be informed by an understanding of the risks and tailored to their values and priorities.”
Reference Source: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/gid-ng10178/documents
Related services available at Fleet Street Clinic:
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being, and recent research has revealed a strong link between sleep and cardiovascular health. A study conducted by the University of Warwick in the UK found that individuals who get 7-9 hours of sleep per night have a lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality compared to those who sleep less or more than the recommended range.
The study, published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, analysed data from over 116,000 participants in the UK Biobank study and found that those who slept less than 6 hours or more than 9 hours had a higher risk of CVD and mortality. These findings add to the growing body of evidence that suggests a link between sleep duration and cardiovascular health.
The exact mechanisms by which sleep affects cardiovascular health are not fully understood, but researchers suggest that it may be related to the impact of sleep on cardiovascular regulation, inflammation, and metabolic function.
It is important to prioritize sleep and aim for the recommended range of 7-9 hours to maintain cardiovascular health.
It’s worth noting that these findings are observational, and more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between sleep and cardiovascular health, but it’s a good indication that sleep plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
To read the full study, continue reading here:
medscape.co.uk – Does sleep duration influence cvd and mortality risk?
Related services available at Fleet Street Clinic:
Sepsis Signs:
World Sepsis Day – 13 September
Sepsis is a global health crisis and affects 27 to 30 million people every year. Out of those affected, 7 to 9 million dies. That’s one death every 3.5 seconds.
Sometimes called the silent killer, Sepsis is a bacterial infection of the blood which can become life-threatening. It is very hard to detect in the early stages, with symptoms similar to many other conditions and illnesses. In the UK alone, around 37,000 people die from sepsis each year.
Thankfully, due to public awareness increasing due to medical bodies and health campaigns, sepsis is being talked about more. As a result, parents and doctors have the condition forefront-of-their mind. The condition is treatable with early recognition and care.
Causes of Sepsis
Bacterial infections are the most common causes of Sepsis. However, Sepsis can also be caused by infections like seasonal influenza viruses, dengue viruses, and highly transmissible pathogens.
Children under 1, the elderly and those with chronic diseases and a weakened immune system are most at risk of sepsis.
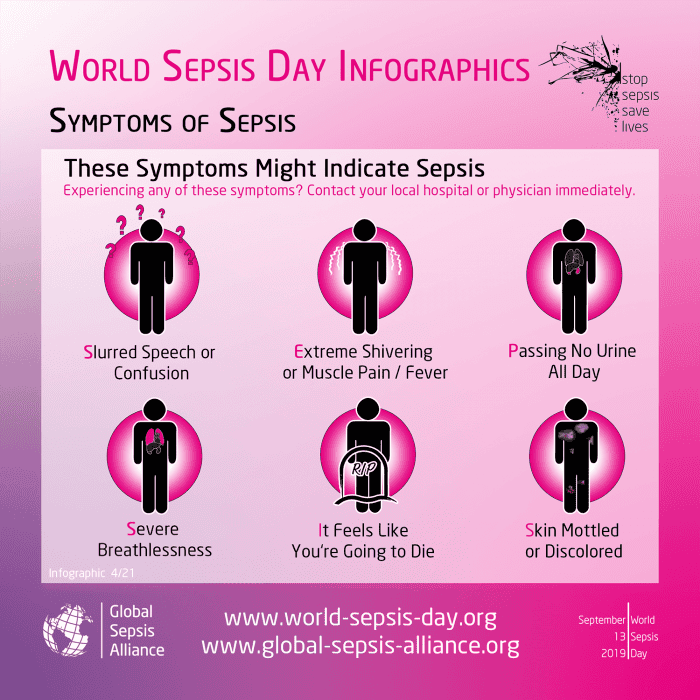
Symptoms of Sepsis
Sepsis can display in a variety of ways including:
-
Slurred speech or confusion
-
Extreme shivering or muscle pain or fever
-
Passing no urine all-day
-
Severe breathlessness
-
It feels like you’re going to die
-
Skin mottled or discoloured
If someone is ill and is getting progressively worse with two or more of the above symptoms, then it is advised for you to go to A & E without delay.
Preventing Sepsis
Preventing infection in the first place is the best way to prevent Sepsis from occurring.
This can be done by:
- Vaccinations – protect yourself from diseases which if serious, could lead to Sepsis.
- Hand Hygiene – reduce the spread of diseases and infections.
- Safe Childbirth – reducing infection to the mother and baby.
- Awareness of Sepsis– knowing the causes and symptoms can save lives.
If you think you are experiencing symptoms of sepsis, you should call 111 as you may require immediate medial attention.
For general GP health checks or vaccinations, you can book an appointment online.
Stoptober is a good time to reflect on smoking habits and how to improve health issues related to tobacco use.
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways you can improve your health and the benefits start almost immediately. And remember, it’s never too late to quit!
The benefits of stopping smoking
After 20 minutes
Blood pressure and pulse are normalised, blood circulation improves.
After 8 hours
Levels of carbon monoxide in the blood decrease.
After 48 hours
Your sense of smell and taste are improving.
After 2 to 3 days
Less or no phlegm in the throat, fewer breathing difficulties.
After 5 to 7 days
Your breath is fresher, your teeth are cleaner and energy levels higher.
After 2 to 3 weeks
Physical withdrawal symptoms will stop, and you can now go several hours without thinking about smoking. Your risk of blood clots (thrombosis) is reduced.
After 4 weeks
Coughing, blocked sinuses and breathing difficulties should subside. The lungs are better able to resist infection.
After 2 to 3 months
Lung function improves by 5%.
After 1 year
The risk of developing cardiovascular disease is halved.
After 2 to 3 years
The risk of developing severe pneumonia or flu is the same as for a non-smoker. Your risk of heart disease, angina (chest pains) and stroke continues to fall.
After 5 years
The risk of throat, oesophageal and bladder cancer is halved.
After 5 to 10 years
The risk of developing cardiovascular disease or thrombosis is the same as for a non-smoker.
After 10 years
The risk of lung cancer is halved. The risk of developing osteoporosis decreases.
After 15 to 20 years
The risk of lung, throat, oesophageal or bladder cancer is the same as for a non-smoker. But heavy smokers (20 a day) have double the risk of lung cancer for the rest of their lives.
Help with quitting
If you need any advice or help to stop smoking, you can book an appointment with one of our GPs.